G2 - unit test
source: AWS
unit testing
- testing the smallest functional unit of code to ensure code quality
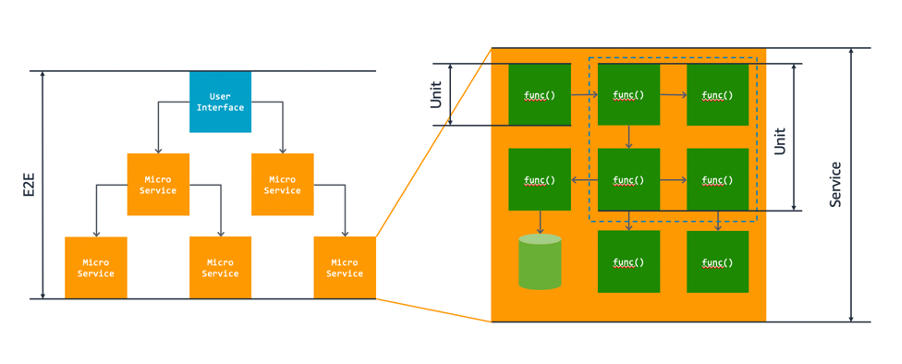
image: AWS
unit test
- a block of code that verifies the accuracy of a smaller, isolated block; typically a function or a method
-
checks if the block works according to the intended logic
-
only interacts with the block via inputs and captures asserts
-
it needs to run in isolation with the rest of the program
-
test cases are a set of unit tests in a single code block
strategies
- logic check
- right calculations
- right path given a correct, expected input
- all paths covered by the given inputs
- boundary checks
- system's response to given inputs
- response to typical inputs, edge cases, invalid inputs
- error handling
- system's response when errors in inputs
examples
## method
def add_two_numbers(x, y):
return x + y
## corresponding unit tests
def test_add_positives():
result = add_two_numbers(5, 40)
assert result == 45
def test_add_negatives():
result = add_two_numbers(-4, -50)
assert result == -54
def test_add_mixed():
result = add_two_numbers(5, -5)
assert result == 0
best practices
- using a unit test framework
- eg: pytest, unittest
- automate
- assert once
- a single true/false outcome for each unit test
- reduces confusion of a failed assert statement in a block of multiple ones
other testing types
- integration testing checks the proper interaction of different parts of the software
- functional testing checks if it passes the system requirement before building
- performance testing checks if it runs to the expected performance requirements (speed, memory size)
- acceptance testing involves manual testing by user groups to see if it performs as required
- security testing checks the software against known vulnerabilities and threats