C1 - method of least squares
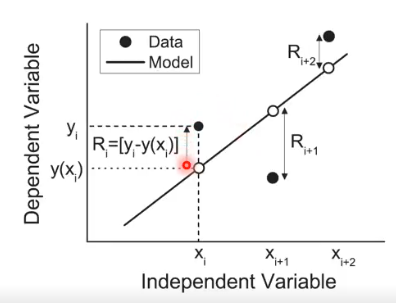
image: TPA Hase, PX271 data analysis course
- the residual of a data point is defined as:
where,
- the method of least squares minimises the sum of the squares of the residuals by changing the slope and the intercept of the line of fit
- the 'goodness of fit' is tested by the chi squared statistic:
- homoscedastic data refers to data with the same uncertainties
- heteroscedastic data refers to data with different uncertainties, hence each point is weighted equally
- normalised residuals weigh the residuals by the uncertainties such that:
- the weighting is inversely proportional to its error
- for poisson data:
where,
-
the data are re-binned such that each interval contains expected counts more than 5
-
equates to confidence limit -
the ellipticity and shape of the error surface around
indicated correlations between the errors and the fit parameters -
this needs to be incorporated into error propagation

image: TPA Hase, PX271 data analysis course