PX285 - H6c - example in a cylinder
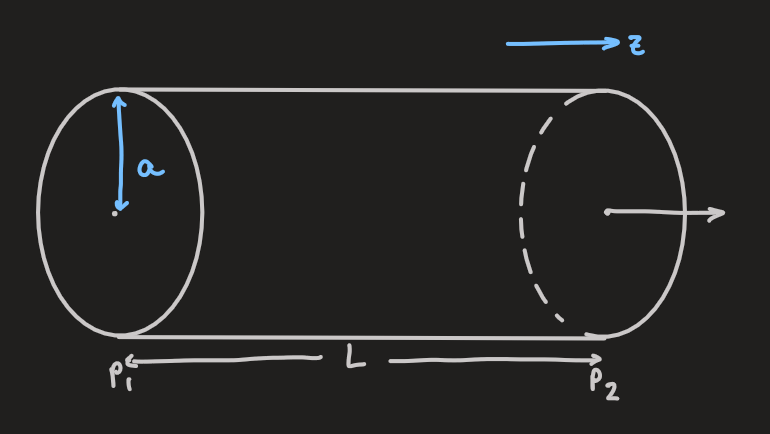
- assuming a laminar, steady and viscous flow:
- considering a fluid element in cylindrical geometry
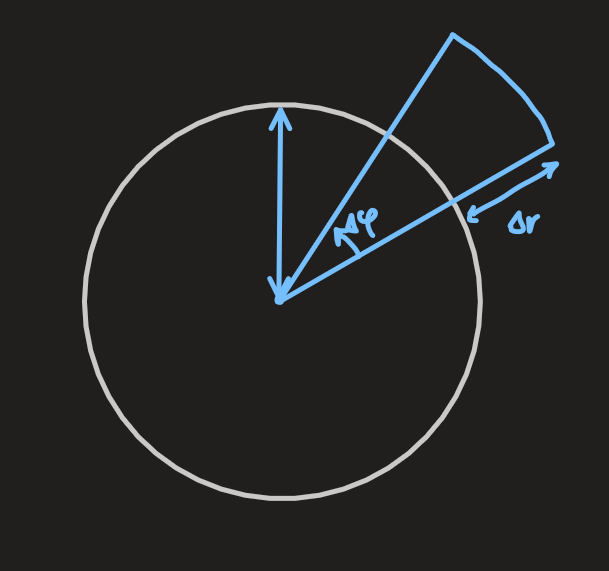
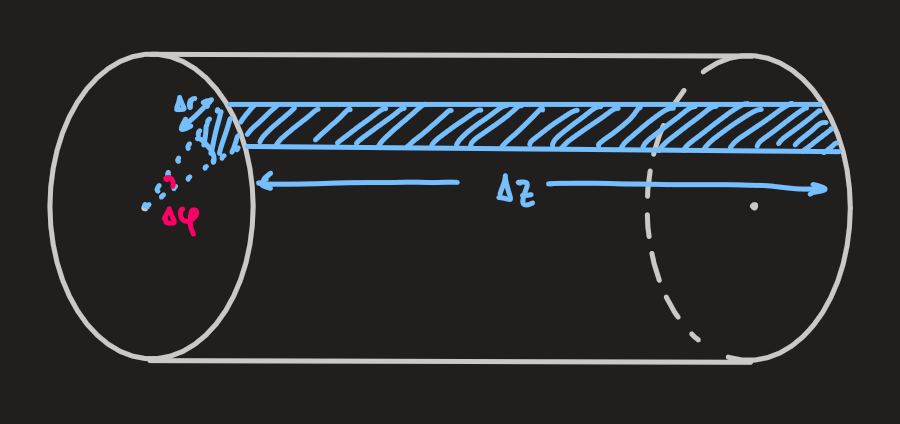
- area of the outer surface:
- area of the inner surface:
- note: areas of the inner and outer surfaces of the chosen fluid element are different (in contrast with the plane case)
- using tayor expansion:
- ignoring all terms in
or smaller:
- the pressure force:
- since it is a steady motion, there is no acceleration, so the net force must be zero:
- integrating twice and applying boundary conditions:
and
- this is again,the poisseuille flow