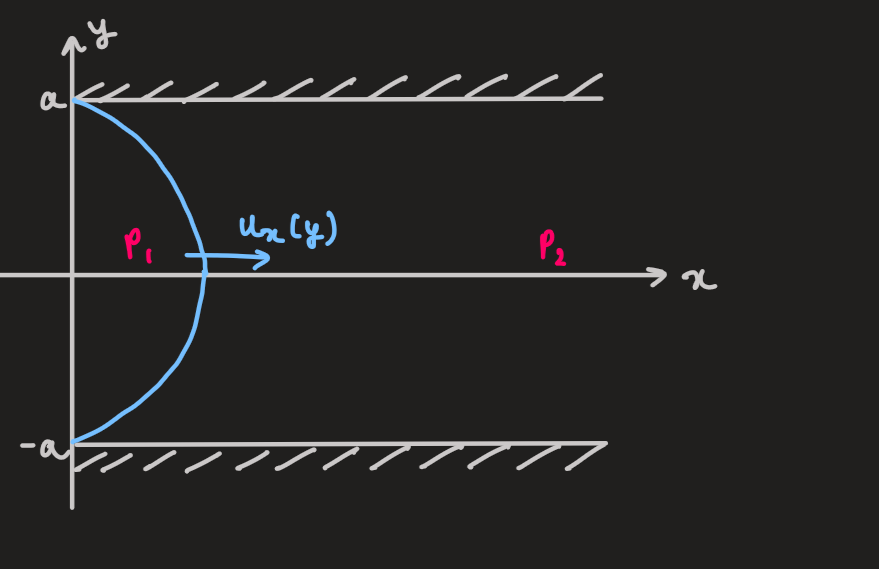
PX285 - H6b - example of a flow
- considering a flow between two parallel plates at
and
- the assumptions:
- laminar (1D,
, no vortices) - steady (time independent)
- viscous (
is important)
- laminar (1D,
- the boundary conditions:
- the steady motion requires a force which counteracts the viscous force
- let it be the pressure difference,
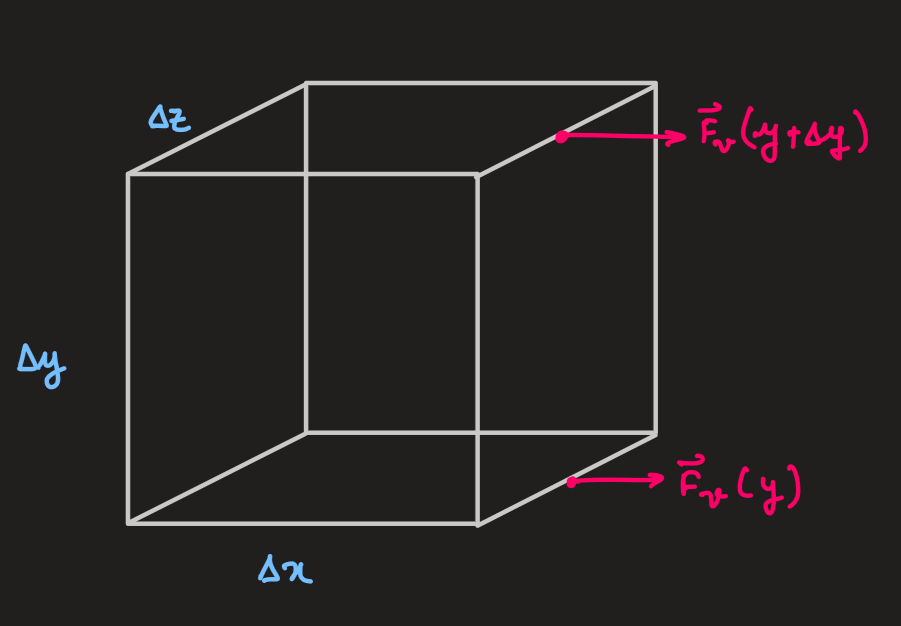
- the viscous force:
where,
- the net force applied at the fluid element:
- as the flow is staedy, there is no acceleration:
-
note: the negative sign vanishes as pressure is decreasing with
, ie. -
from the RHS:
- using the boundary conditions
- constant
comes from the pressure difference - using the LHS:
- therefore, the form of the flow is parabolic, called the poisseuille flow