PX285 - H1 - fluids
definition
- fundamentally, fluid is a substance which fills up a vessel with no fixed shape
- the molecules in a fluid are not fixed in a lattice like in solids, and they are able to move freely relative to each other
methods of describing fluids
considering every molecule
- each molecule has a velocity,
- kinematic equations from the newton's second law give the trajectories of the molecules
- it works if there are a small number of molecules
kinetic approach
- using a distribution function,
, that gives the number of molecules at a certain location (a sufficiently small volume) with a certain velocity (a small interval of velocities) at a certain time - the boltzmann equation such a function, but it is a 7D problem
continuous matter approach - fluid/hydro-dynamics
- introducing density:
- more rigorously:
- from quantum mechanics, it is known that
cannot approach 0 - as
, there are fluctuations below a certain volume, , in due to discrete nature
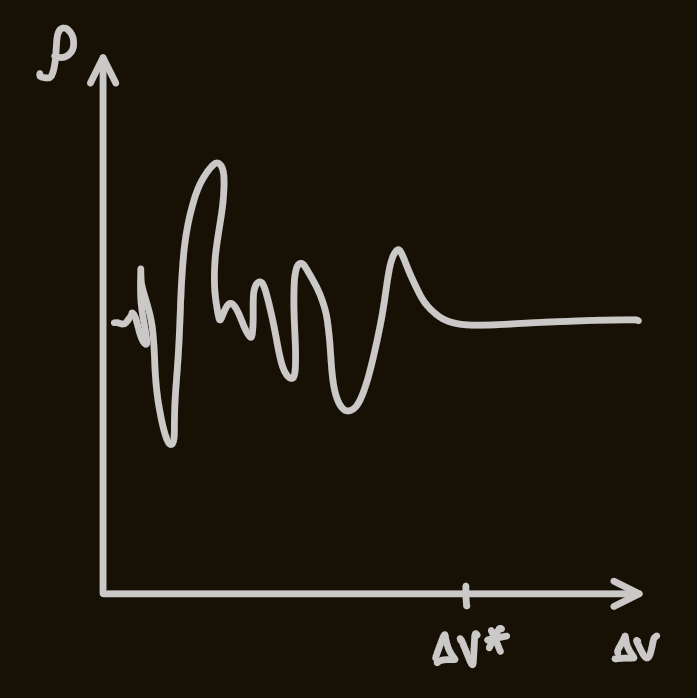
-
for water, air, etc, in atmospheric pressure,
mm -
for scales smaller than
mm, fluid mechanics works -
defining the knudsen number:
where,
-
mean free path is the average distance that a molecule travels between two collisions
-
if
, fluid approach is justified -
at atmospheric pressure,
m -
at
km height above the ground, cm