PX284 - T3b - spherical surface using intersecting cords theorem
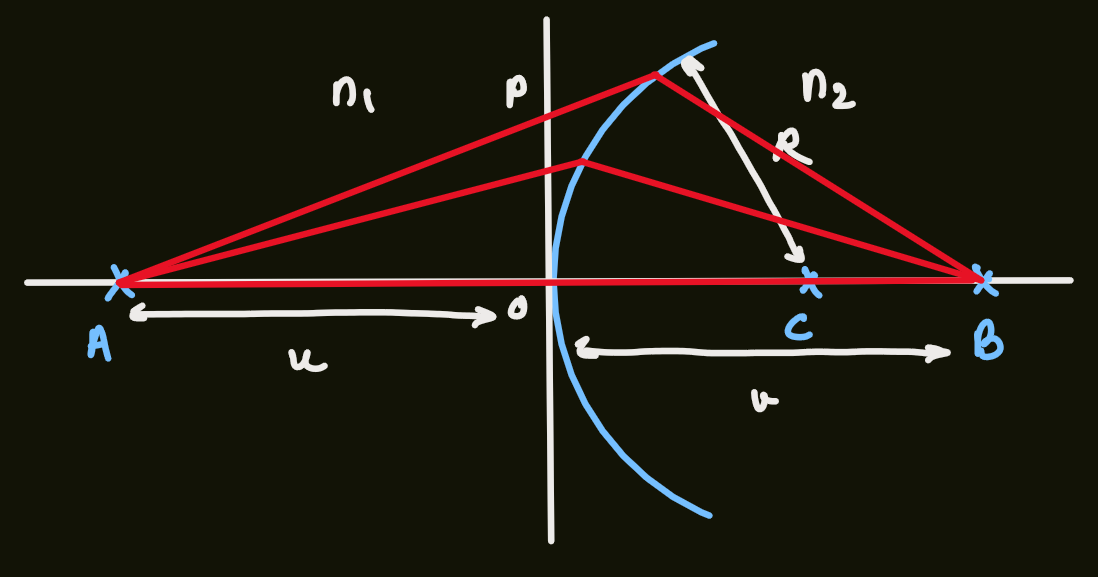
- considering a spherical surface using 'real is positive' convention (
and ) - the optical path length
intersecting cord theorem
when any two cords on a circle cross, the products of the length of the two pieces of each cord are equal
- from fermat's principle:
- limiting to 'paraxial rays', where the rays lie at small angles to the axis, so
is small, AKA gaussian optics:
- if the spherical surface curved the other way,
- this is equivalent to setting
, referred to as 'negative radius of curvature'