PX284 - Q3 - maxwell's equations in matter
- the charge density can be separated into two components: free and bound
- also, the current density has two components:
- the solenoidal condition remains unchanged:
- faraday's law does not involve
or , so it remains unchanged as well:
- gauss' law:
is called the 'displacement', and gauss' law can be rewritten as:
- ampere-maxwell law:
is called the 'magnetic field strength', and is called the 'magnetic flux density'
- the complete set of maxwell's equations in matter:
- for the electric case:
- isotropic:
- linear:
- for the magnetic case:
where,
- isotropic:
- linear:
and may be freqency dependent - eg: water molecules (H
O) - the atoms are aligned at an angle, so there is a dipole
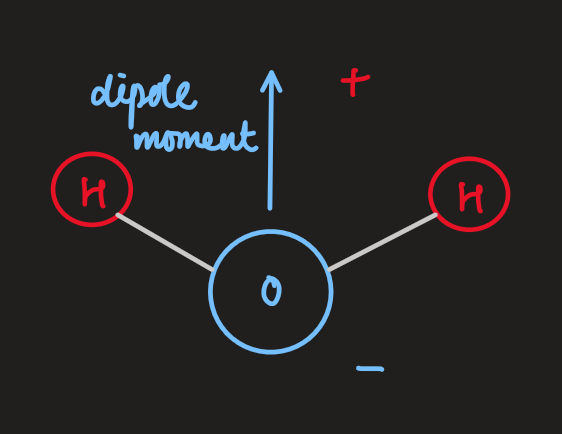
- in the absence of an electric field, the dipole moments have random orientations due to thermal motion, giving a net zero dipole moment
- when an external field is applied,
, the diploes align with the field, giving a net polarization along the direction of
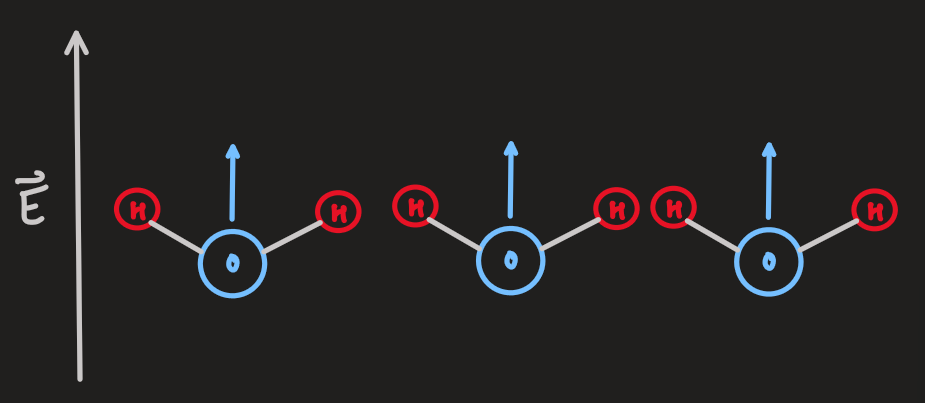
- if
is oscillating, molecules/ions need time to reorient themselves, which is les possible at high - therefore,
and , and and