PX284 - H3 - distinguishability
- considering a single particle in a two-state system
- there are two possible configurations:
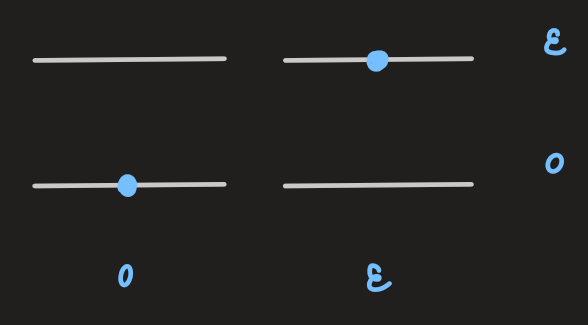
- now, considering two distinguishable particles in the same system:
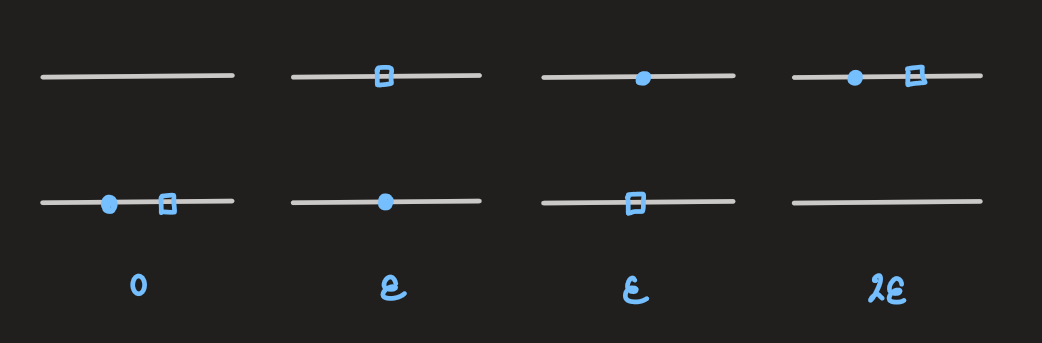
- similarly, for
distinguishable particles:
- now, considering two indistinguishable particles:
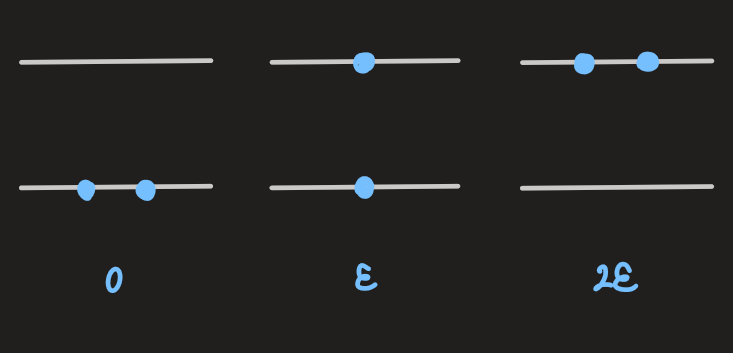
- therefore, for indistinguishable particles:
- in fact,
overcounts the number of states in which particles sit in different energy levels by a factor of
provided that the configurations wherein more than one particles are in a state can be neglected
- this can only be done if
, ie. no wavefunction overlap, so a classical gas
| example | type |
|---|---|
| H |
indistinguishable |
| spins on a regular lattice (paramagnets) |
distinguishable |