PX282 - K2a - interiors of gas giants
- the radius vs mass can be calculated for a given composition by assuming hydrostatic equilibrium
- balancing gravity with pressure gradient:
where,
- to solve for
, is needed, so the equation of state is needed - this can be very complex and difficult to measure at high pressures
- but for H and He, it can be assumed that:
where,
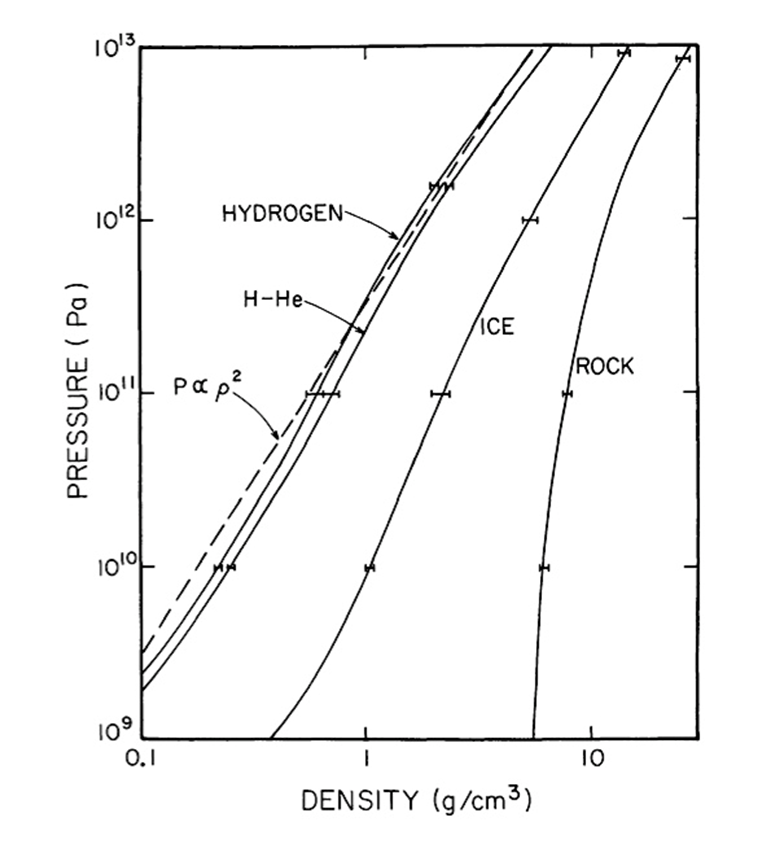
image: Stevenson 1982, AREPS 10, 257
- using the mass conservation equation, for a small shell of radius
where,
- to find the radius of a planet, where
, which occurs when:
- for jupiter, it is found that
m, which is (a really good simple approximation)
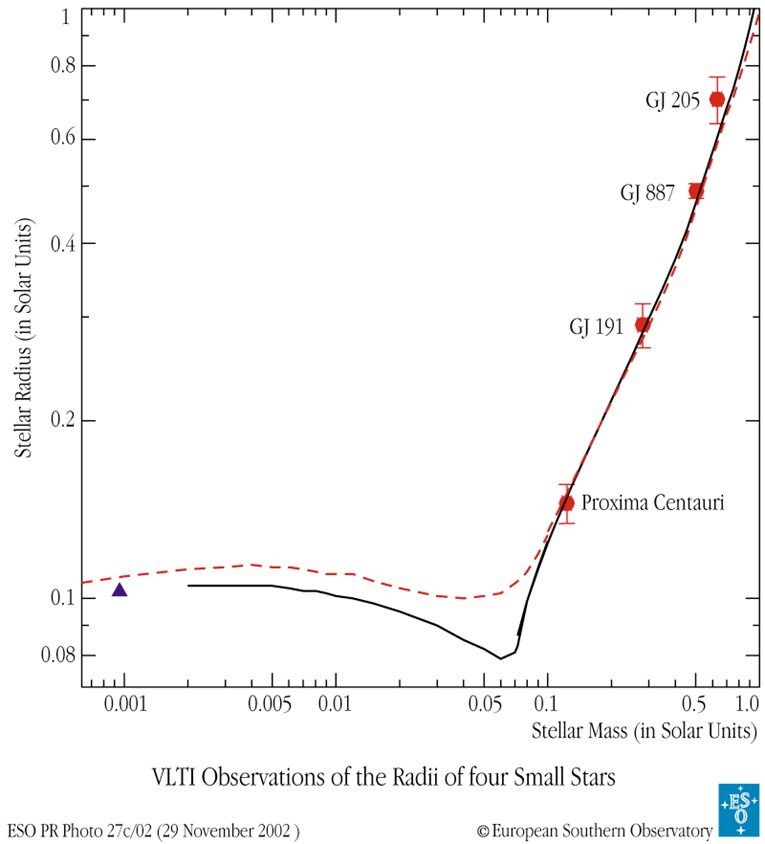
image: ESO 2002
- for central density,
, integrating the mass conservation equation:
- integrating by parts, and
-
for jupiter,
kg m -
H/He gas with density similar to rock
-
from the equation of state, the central pressure:
-
the real phase diagram of H implies a metallic liquid at this pressure
-
the electrons are no longer localised to individual atoms, and it conducts electricity - metallic hydrogen
-
expect a rocky icy core, then a layer of metallic hydrogen
-
higher up in the envelope, H transitions to molecular fluid
-
saturn should have the same layers
-
but due to lower pressure, the metallic layer is smaller
-
possible 'rain out' of He, as it forms droplets due to no longer being soluble in H, which drives ongoing differentiation and heating
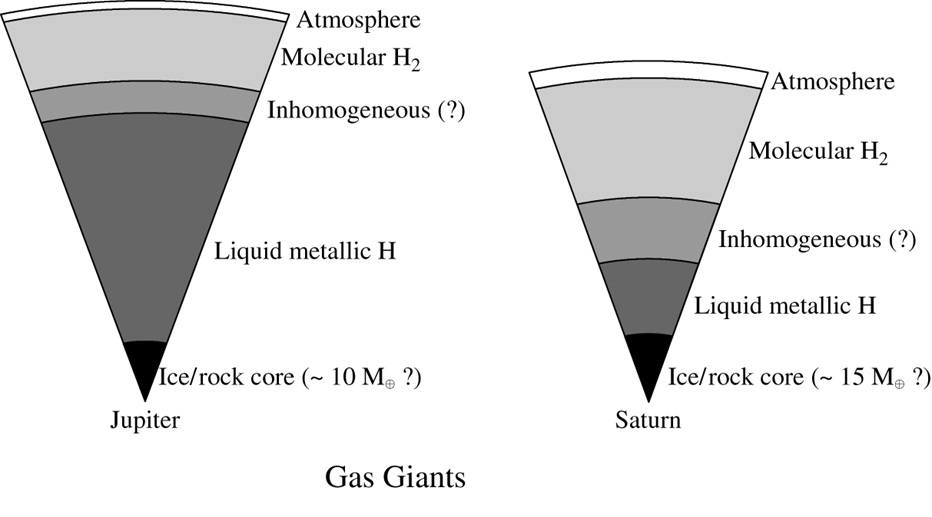
image: Carroll & Ostile, An Introduction to Modern Astrophysics (2007)
- both of them rotate rapidly (
day, which makes them oblate - this breaks their spherical symmetries
- so, the gravitational potential probes the interior structure
- eg: samples with juno mission are used for the measurement of
, and also north-south asymmetries - the banding pattern extends into deep interior, which implies a global convection
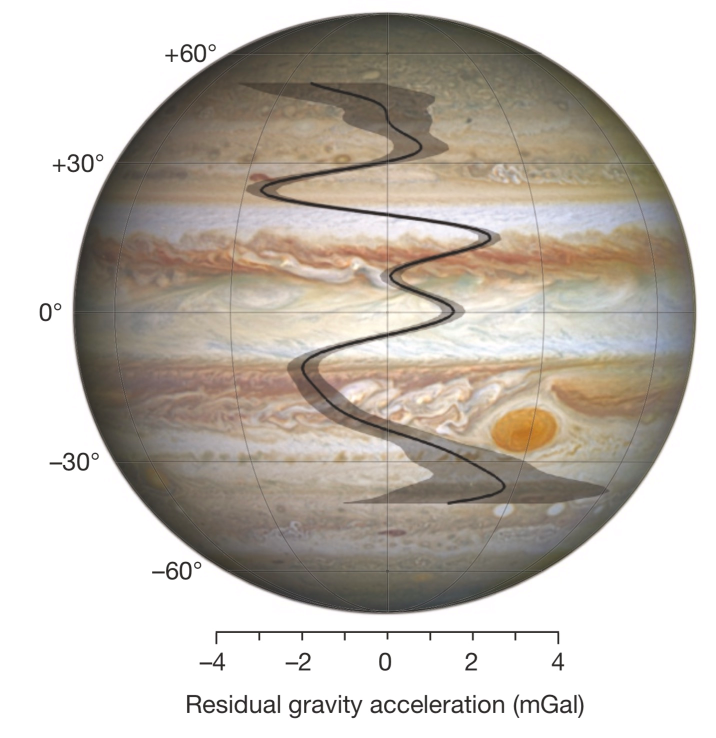
image: IESS, et al 2018
-
convection, rotation and conducting (metallic) interior forms a magnetic dynamo
-
therefore, jupiter has a strong magnetic field
-
the magnetic moment of jupiter
that of earth -
the magnetic moment of saturn
that of earth, due to less metallic H -
the strong magnetic fields lead to aurorae in poles, as well as radio emissions via both cyclotron and synchrotron emissions by low and high energy electrons orbiting the magnetic field lines
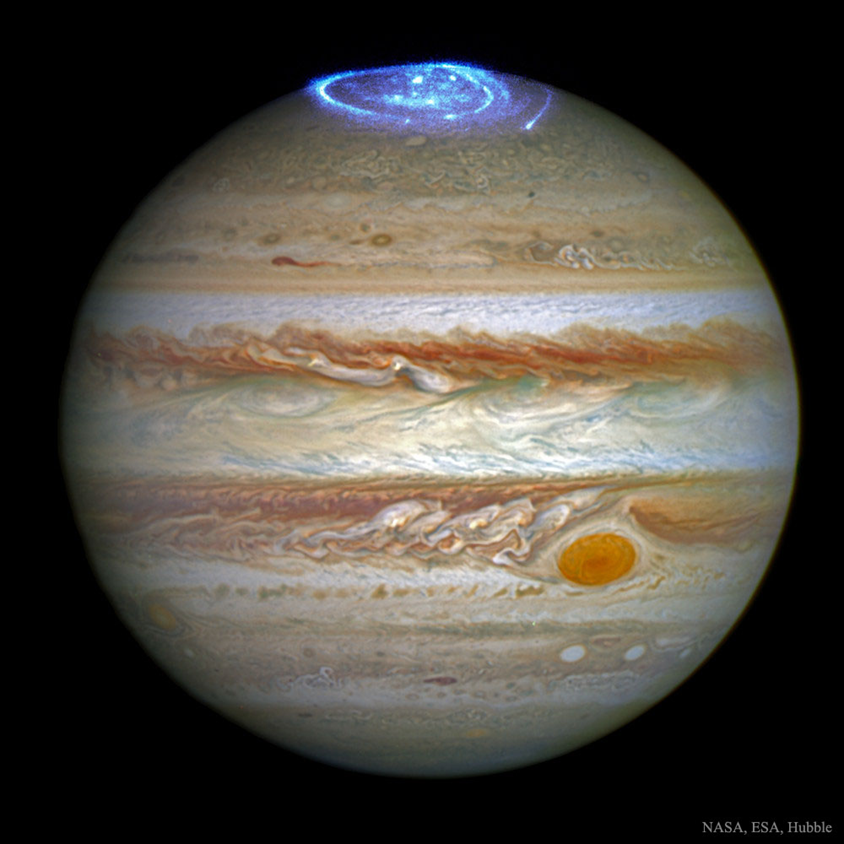
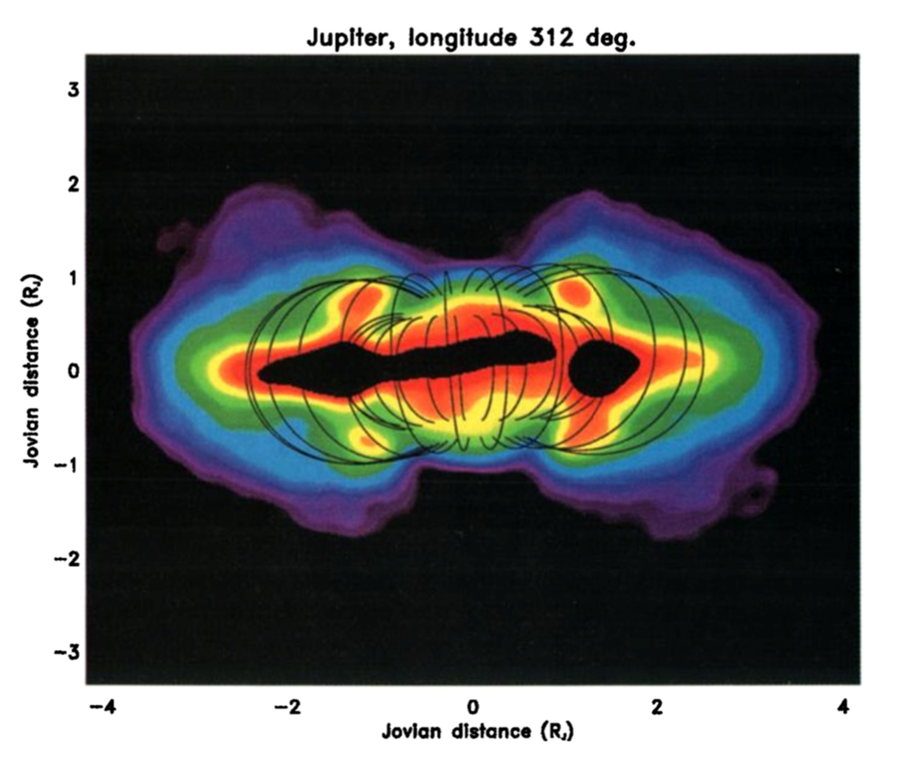
image: de Pater, et al 1997
- the combination of strong magnetic moment and lower solar wind flux at
au leads to a very large magnetosphere - the extent can be estimated by equating magnetic energy density
with the kinetic energy density of solar winds
- for a magnetic dipole:
where,
where,
- this can easily be scaled between planets:
where,
- the magnetic dipole moments:
, and the orbital separations: - so, jupiter's magnetosphere is the largest object in the solar system