PX282 - I2 - kepler's laws
first law
a planet orbits the sun in an ellipse, with the sun at a focus of the ellipse
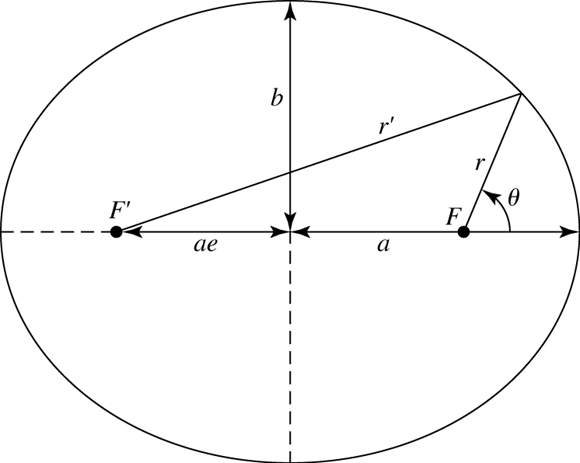
image: Carrol & Ostile, An Introduction to Modern Astrophysics, 2007
- mathematically, an ellipse is described by:
where,
also,
- considering a point,
, on the perimeter:
conic sections
| eccentricity | shape |
|---|---|
| circle | |
| ellipse | |
| parabola | |
| hyperbola |
- all these shapes are allowed orbits
second law
a line connecting a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal time intervals
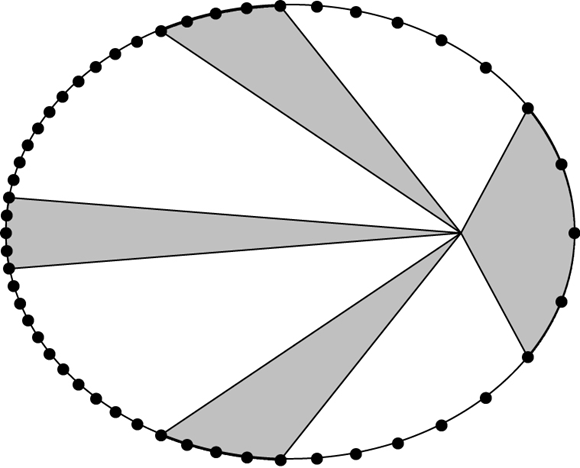
image: Carrol & Ostile, An Introduction to Modern Astrophysics, 2007
third law
the orbital period
-
therefore,
gives the relative distance from the sun -
eg:
-
by measuring the parallax of transit of venus, the value of an astronomical unit was determined to
of the modern value (1769,1771) -
modern value is determined from radar measurements of venus