PX282 - D7 - PP1 fusion chain
- considering the hydrogen-fusion reaction:
- governed by conservation laws:
- electric charge
- nucleon number
- lepton number
- energy and momentum
- it is detailed in the PP1 chain, which is the most common in the sun
- starts with the formation of deuterium:
- here, a proton has decayed into a neutron:
- next:
- overall:
energy released
- the reaction rates are set by the slowest process
- for PP1, the initial decay of
requires the weak nuclear force and collisions, and it takes years for a given proton - energy is needed to overcome the strong nuclear force and escape the coulomb potential well
- comparing the thermal and the coulomb energy:
-
the required temperature for this case would be
, this is too high, and it can be concluded that the thermal energy is not enough -
the only way this can happen is due to quantum tunnelling
-
according to the uncertainty principle
can be large enough to 'cross the gap' - reaction ratios:
where,
- the probability of tunnelling:
- the velocity:
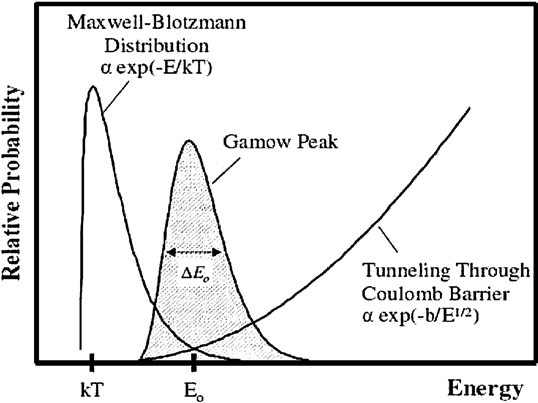
image: livius trache
- expanding the exponentials:
where,
- the energy generation rate per unit mass:
other reactions
- CNO cycle
for - the core gets denser as the reaction progresses, causing it to shrink and get hotter
- at high enough temperature,
can fuse
- triple
reaction:
-
- the energy gets progressively lower, thus less time is taken for subsequent fusions into heavier nuclei