PX282 - D6 - nuclear binding energies
- the energy of an atom:
where,
- this inequality shows that there is an energy difference, called the 'binding energy'
- the binding energy is the amount of energy required to separate the components of an atom:
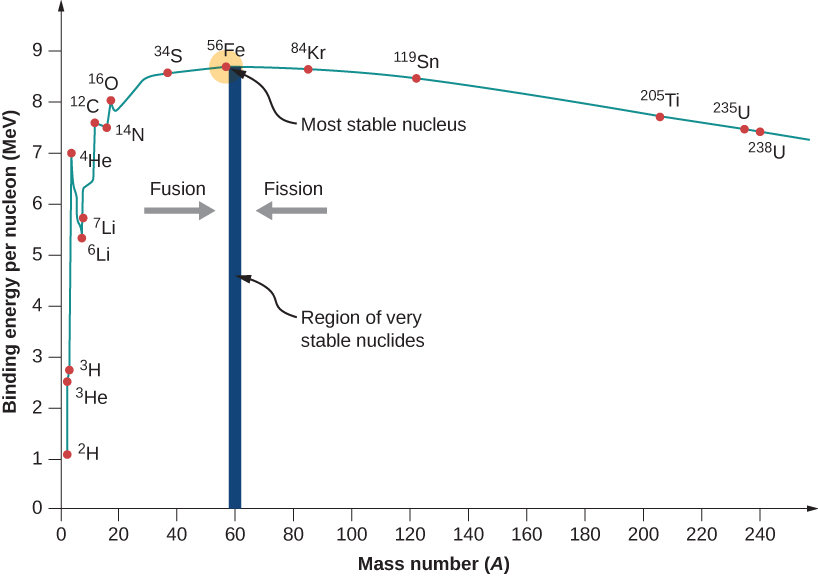
image: david moriaf
- consider a fusion reaction:
-
the energy released:
per nucleon -
going past He gives energy, whereas going past Fe costs energy
-
Fe is the most tightly bound per nucleon
-
eg:
- using the atomic mass unit:
and - the mass of individual nucleons:
- the mass of the atom:
- the mass difference:
- the binding energy:
- using the atomic mass unit:
-
eg:
- the mass difference:
- the binding energy:
- the mass difference: