PX282 - C9g - combined opacity
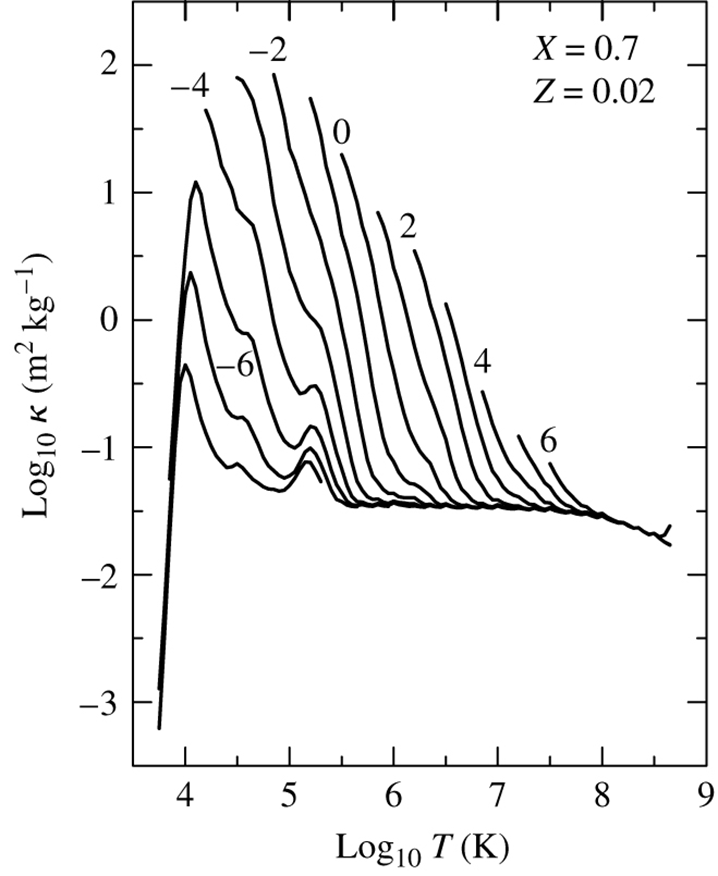
image: iglesias & rogers (1996)
-
three key zones are seen
-
low temperatures opacity rises steeply as the number of free electrons rises with , which are needed to make - this is a combined opacity, ie: average across wavelength and opacity sources
-
medium temperatures, , - the decay comes from kramer's law:
- driven by b-f and f-f absorption
- the decay comes from kramer's law:
-
high temperature - all electrons are free, and everything is ionized
- converges to a constant equivalent to the thomson scattering coefficient