PX262 - J3 - molecules
- approximation: neglecting the kinetic energy of the nuclei and solving the electronic problem
- nuclei take the positions where the sum of electronic energy and nuclear coulomb energy is minimized, electrons bond the nuclei
- types of bonding:
- covalent
- ionic
- considering a covalent bond in H
- the two protons are fixed at
and , and the two electrons at and - the distance from
to - building a model of the electrons' ground state from hydrogen states which complies with the pauli exclusion principle
covalent bond
- for one hydrogen atom:
where,
- in the molecule, approximating the ground state two electron wavefunction:
- the charge is concentrated between the protons and each electron is more delocalized than in an isolated atom
is the bond length in the H molecule Å
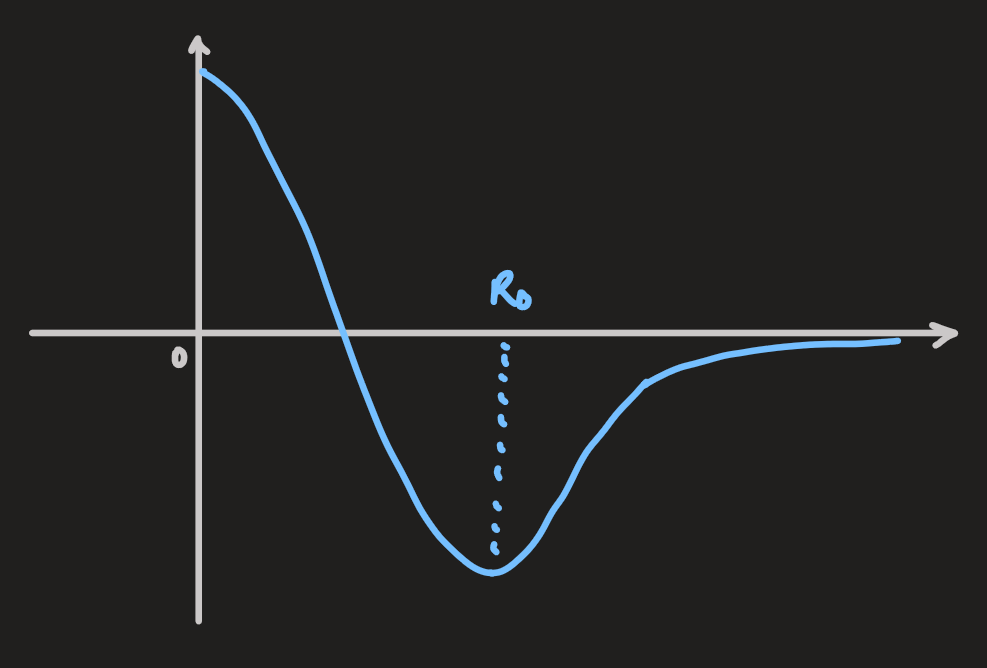
ionic bond
-
for a NaCl molecule:
Na :
Cl : -
the molecule is well described by the Na
valence electron transferring to the Cl shell so that both atoms have filled shell configurations -
Na becomes positively charged, and Cl, negatively
-
this is called an ionic bond