PX158 - E2 - extended objects
- includes galaxies, comets, planets
- surface brightness
flux per angle magnitude / arc-second - brightness in the telescope:
where,
- "
" means - a "slow" focal ratio is a high number, and a "fast" focal ratio is a low number
- fast optics are difficult and quite expensive to make
angular magnification
- due to the wave nature of light, diffraction occurs in telescopes
- bessel found that the diffraction limit for a circular aperture as:
-
eg: what is the minimum angular resolution of the human eye?
- this is the limit, but more typical value
- this is the limit, but more typical value
-
eg: what is the
for the VLT?
-
for ground based telescopes, the atmospheric turbulence limits the angular resolution. this effect is called "seeing"
-
a good site will have "seeing"
-
adaptive optics can help correct this effect using deformable mirrors
adaptive optics
- measuring the 'blurring' due to earth's atmosphere (by bright stars and/or laser guide stars) and correct it via deformable mirrors (millisecond corrections)
- telescopes are situated on high mountains to reduce these effects of earth's atmosphere
- space telescopes do not suffer from this effect but they are very expensive to create, launch, and operate
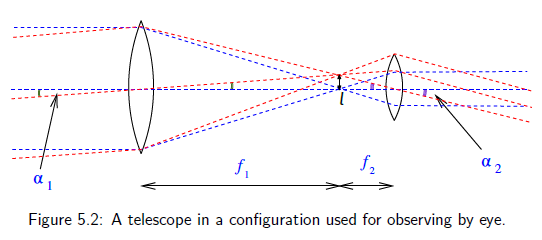
- eg: what is the angular magnification for celestron,
, , ? what is the diffraction limit?