PX158 - B1 - introduction
-
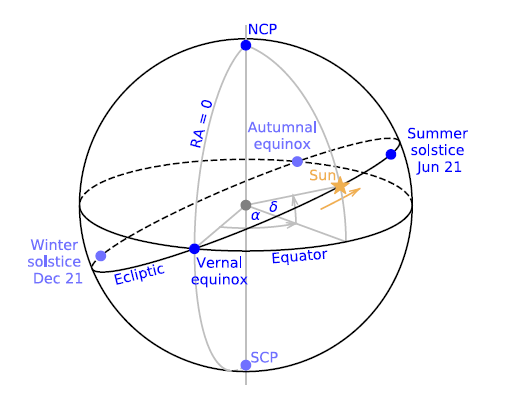
the "celestial sphere" is a way of mapping the position and movement of stars, sun, moon, planets, etc
-
a reference grid similar to latitude and longitude on earth is used
- right ascension (R.A.)
- equivalent to longitude
to , sometimes to
- declination (Dec.)
- equivalent to latitude
to
- right ascension (R.A.)
-
it can be observed that all the stars in the night sky rotate about a point called the celestial pole (approximately polaris for the northern hemisphere)
-
it rotates once per day
-
the positions of stars in the reference grid remain unchanged
-
the positions of the sun and the planets change throughout the year.
-
the sun move along the great circle called the ecliptic, and the planets move very close to it. the moon also moves very close to it
-
the position of the sun for the northern hemisphere:
- at the vernal equinox (
):
- at the summer solstice (
):
- at the autumn equinox (
):
- at the winter solstice (
):
- at the vernal equinox (
-
the sun rises and sets due east and west respectively on the equinoxes, and at the extreme north/south positions on the solstices