PX157 - B12a - dielectrics
introduction
- in a dielectric (insulator), there are only bound charges if no excess charges have been applied

- subjecting a dipole to an electric field, the positive and negative charges in an atom are displaced slightly in opposite directions
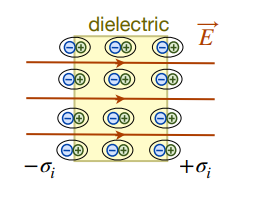
- surface charges are induced by the external electric field,
, which induces an electric field, , that opposes
dielectric breakdown
- if the external electric field,
, is strong enough, it can ionize the atoms free charges no more dielectric - the maximum electric field that a dielectric can withstand is termed the dielectric strength,
- dry air:
- pyrex glass:
- dry air:
- polarization density
:
- electric displacement vector
:
and are along the same direction