PX157 - B9 - potential gradients
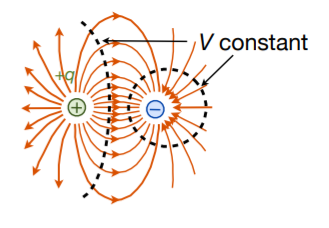
equipotential surfaces
- surfaces of constant potential
- from here:
- assume that the points,
and , are infinitesimally close:
- assume that the points,
and lie on the same equipotential surface:
is tangential to the equipotential surface. hence, is perpendicular to the equipotential surface
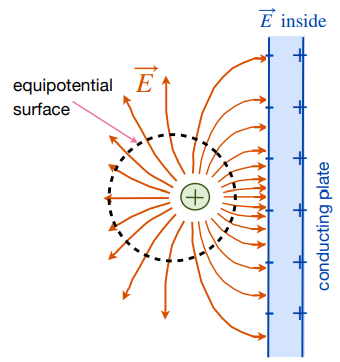
- in a conductor,
, and equipotential volume
potential gradients
- from here:
- this is true also if
and are infinitesimally close:
- in
D:
- in
D:
, and
- eg: a ring of charges
and because expect an extremum (minimum/maximum) on x-axis
&= \frac{Q}{4\pi\epsilon_{0}} \frac{x}{(x^{2}+a^{2})^{\frac{3}{2}}} \hat x
\end{align*}$$