PX155 - classical mechanics - summary
A - foundations of classical mechanics
newton's laws
first law
- law of inertia
- "every body continues in its state of rest or uniform motion unless acted on by an external force"
second law
- "the rate of change of momentum of a body is equal to the total external force acting upon it"
- if mass is constant:
third law
- "to every action there is an equal and opposite reaction"
friction
static friction
kinetic friction
gravitation
newton's law of gravity
newton's shell theorem
- force on a mass outside the shell due to the shell is as if it is due to a point mass at the shell's centre
- force on a mass inside the shell is zero as the net force is zero
B - systems of particles and acceleration
centre of mass
equations of motion
constant acceleration
time-dependent acceleration
position-dependent acceleration
velocity-dependent acceleration
C - work and energy
kinetic energy
conservative forces
- conservative if work done is independent of the path
gravitational potential energy
- considering
- gravitational potential:
power
D - simple harmonic moton
general equation
- angular velocity:
where,
energy
complex form
where,
$$\ddot z + \omega^{2} z = 0$$
damped oscillations
where,
$$\ddot z + \gamma \dot z + \omega^{2}z =0$$
$$\lambda = - \frac{\gamma}{2}\pm \sqrt{\left(\frac{\gamma}{2}\right)^{2}-\omega^{2}}$$
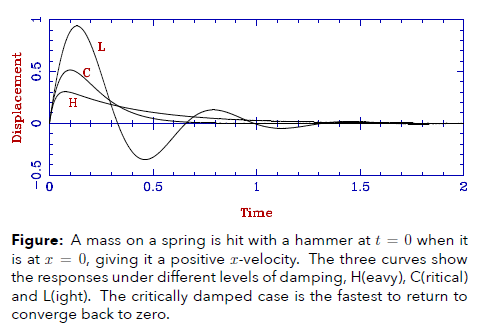
light daming
heavy damping
critical damping
driven damped oscillations
- trying
E - circular motion, rotation of bodies
circular motion
angular velocity (
centripetal acceleration
moments
- for a system in equilibrium, sum of moments about a point is zero
torque (
angular momentum
-
for a particle moving in a straight line,
along any point not along the straight line -
for a lever to balance, about the fulcrum,
-
for a moving particle:
orbital angular momentum
- for a satellite of mass,
, orbiting earth at a distance, , from the centre of earth:
- angular momentum is conserved
moment of inertia (I)
- which is not true if:
- plane of rotation does not contain the origin of
- the origin is not the centre of rotation
- plane of rotation does not contain the origin of
for continuous rigid bodies
- for a thin ring with radius,
, and mass , about an axis perpendicular though its centre, let the mass per unit length along the circumference be
- for a uniform disc with radius,
, and mass , about an axis perpendicular though its centre: - dividing the disc into concentric rings of radius,
, and thickness, , is the mass per unit area such that the mass of the ring,
- dividing the disc into concentric rings of radius,
- for a hollow sphere about an axis through its centre:
- for a solid sphere about an axis through its centre:
- for a thin uniform rod about an axis perpendicular though its centre:
- for a thin uniform rod about an axis perpendicular thought one end:
parallel axis theorem
- axes about which
and are taken must be parallel