PX154 - E4 - the carnot cycle
introduction
- introduced by sadi carnot in 1834 as an ideal model of a reversible heat engine cycle
- it's theoretical and it can be shown that it's the most efficient heat engine cycle
- all real engines have an efficiency lower than that of a carnot engine
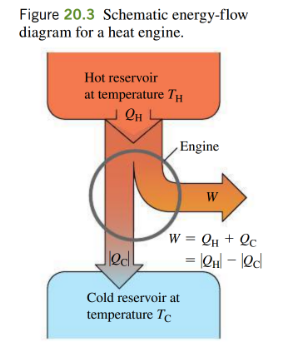
- work done = area enclosed by the cycle
- if this is reversed, a heat pump would be created
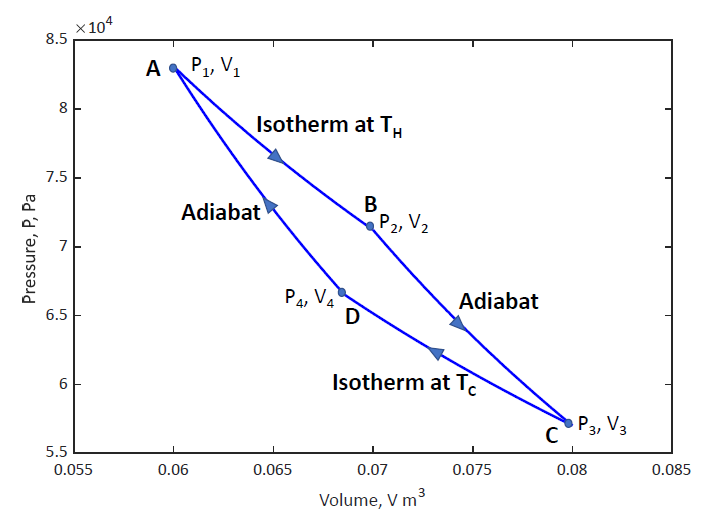
work done in the carnot cycle
-
isothermal expansion at
-
adiabatic cooling
-
isothermal compression at - heat expelled from engine to the cold reservoir
- heat expelled from engine to the cold reservoir
-
adiabatic compression
-
for one cycle:
-
can simplify using:
, for adiabatic process - for
- for
- so:
- for
efficiency of the carnot cycle
[YF 20.6]
- we have:
heat absorbed from heat expelled from
- just showed that
:
-
eg:
, , , , - petrol engine
- diesel engine
- stirling engine
- humans
-
always use kelvin for temperature
-
all reversible engines operating between the same temperatures have the same efficiency