PX154 - B2 - thermal expansion

thermometer
- heating causes expansion
- liquid rises up the tube as the temperature increases
- but the glass expands too
- most materials expand as they heat up but different materials expand by different amounts
- we define the expansion coefficient
- we define the expansion coefficient
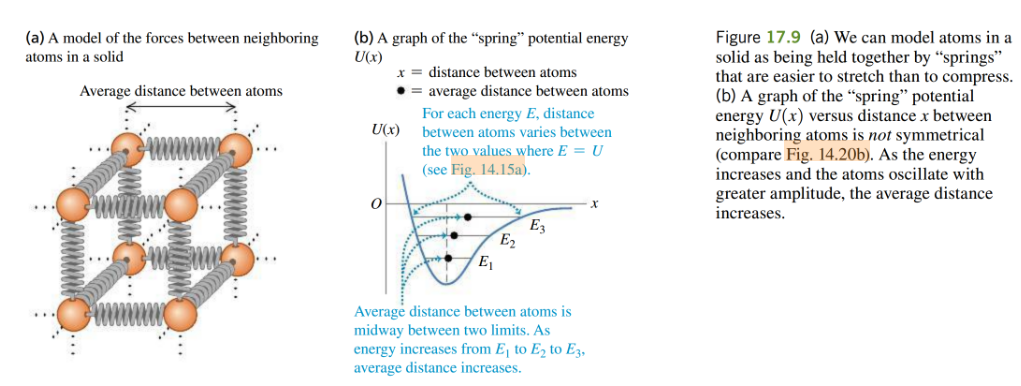
- why do materials expand?
- as the temperature increases, the mean atomic separation increases (atoms vibrating about the mean position)
linear expansion coefficient

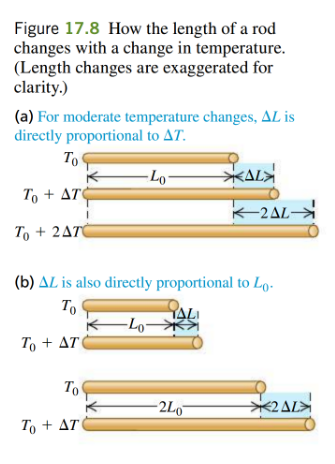
- [YF17.8]
- new length:
can be defined in terms of the change in temperature - where
linear expansion coefficient
- where
- works for moderate temperature changes
- then we define
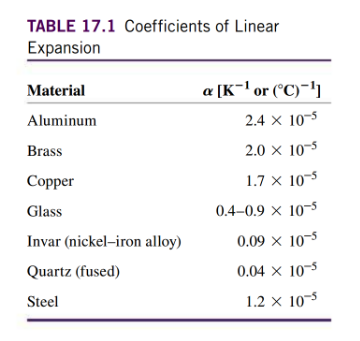
- its units are - eg: [YF table 17.1]
volume expansion coefficient
- in the same manner as in linear expansion coefficient, we can define the volume expansion coefficient:
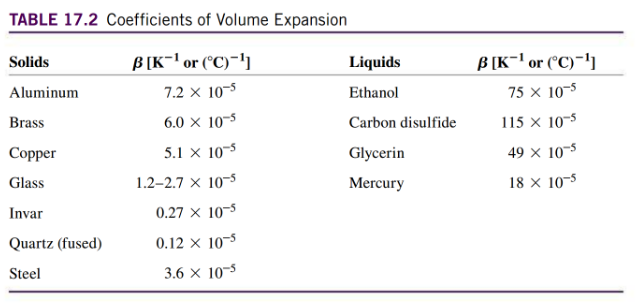
- eg: [YF table 1.2]
- can see
- [YF P576] for derivation: 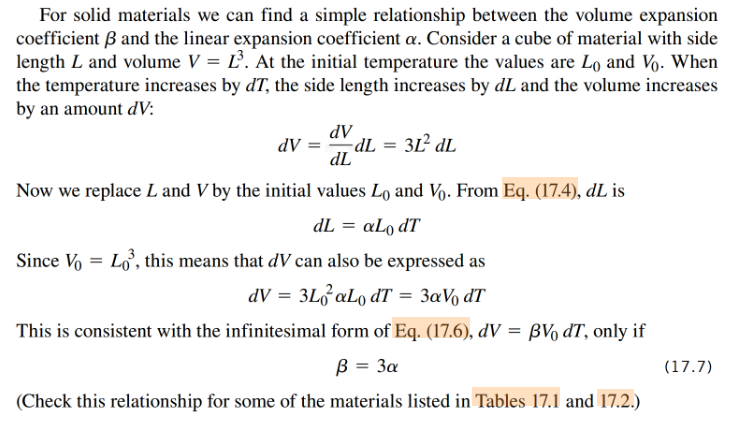
- comments:
- we are considering isotropic materials which have the same properties in different directions
- we are assuming that the coefficients
- some materials have odd behaviour
- eg: water near