PX153 - A5 - coordinate systems
- recall [basis vectors](PX153 - A1 - notation and geometrical representation)
- in 3D, a coordinate system can be defined by specifying 3 linearly independent basis vectors at every point in space
- usually defined to be orthonormal
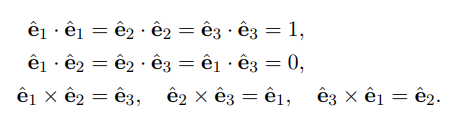
- to find
, several ways - eg: tangent to the curve marking the change in coordinate
cartesian coordinates
circular polar coordinates
- 2D
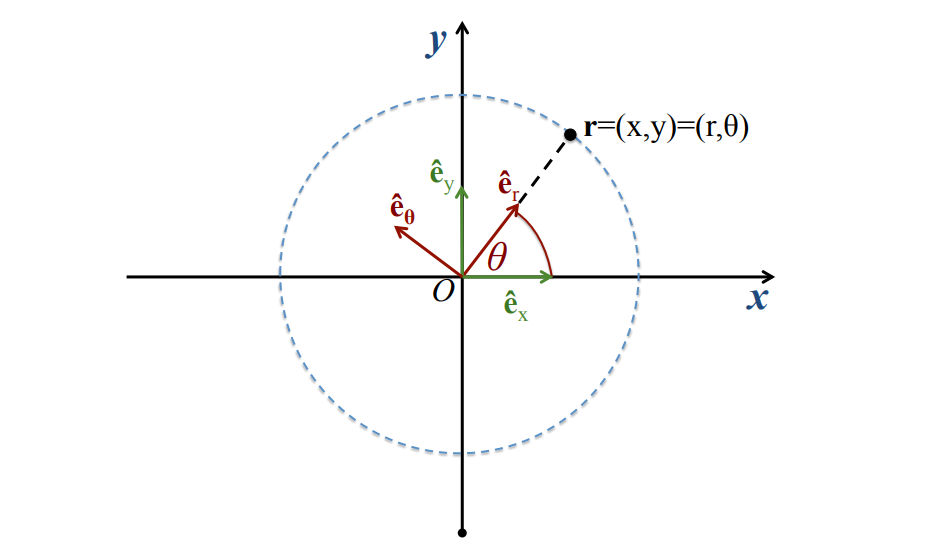
- here,
is the magnitude of the vector and is the angle made by the vector with the x-axis in counter-clockwise direction such that or
- here,
- transforming between polar and cartesian coordinates:
- the basis vectors for polar coordinates vary in space, but are always orthonormal

- to check: these are orthonormal
cylindrical polar coordinates
- 3D
- polar coordinates in x-y plane, extend by keeping the z-axis
- defined by
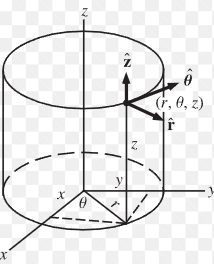
- defined by
- transformations to/from cartesian:
spherical polar coordinates
- 3D
- defined by
- defined by
- for problems with spherical symmetry
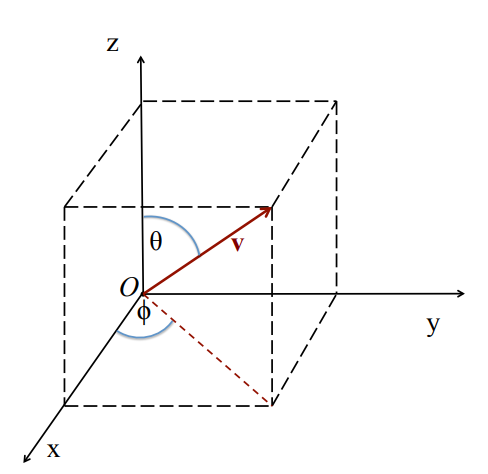
- transformations to/from cartesian:
again,, , vary in space