PX153 - A1 - notation and geometrical representation
scalar
- a scalar quantity is defined by its magnitude
- independent of coordinate system
- eg: density, speed
vector
- has a magnitude and direction
- components depend on the coordinate system
- geometrically, it's an arrow, length proportional to the magnitude
- for vectors, in books, often in bold v
- often underlined / with an arrow on top
- magnitude is given by :
- direction is often described by a unit vector (underlined with a hat on top)
- any vector can be written as:
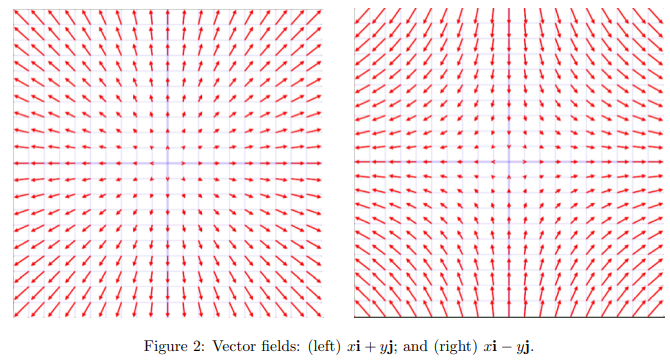
vector fields
- describes a vector that varies continuously in space
- eg: wind - has a magnitude (speed) and a direction that vary continuously with position